CHARGE syndrome
Home / CHARGE syndrome
Case Title
CHARGE syndrome
Clinical History
Imaging Findings:
Discussion :
Background : “ CHARGE” syndrome is a rare foetal congenital disorder that affects multiple organ systems and that classically
describes a combination of head and neck, cardiac, CNS and genitourinary disorders:
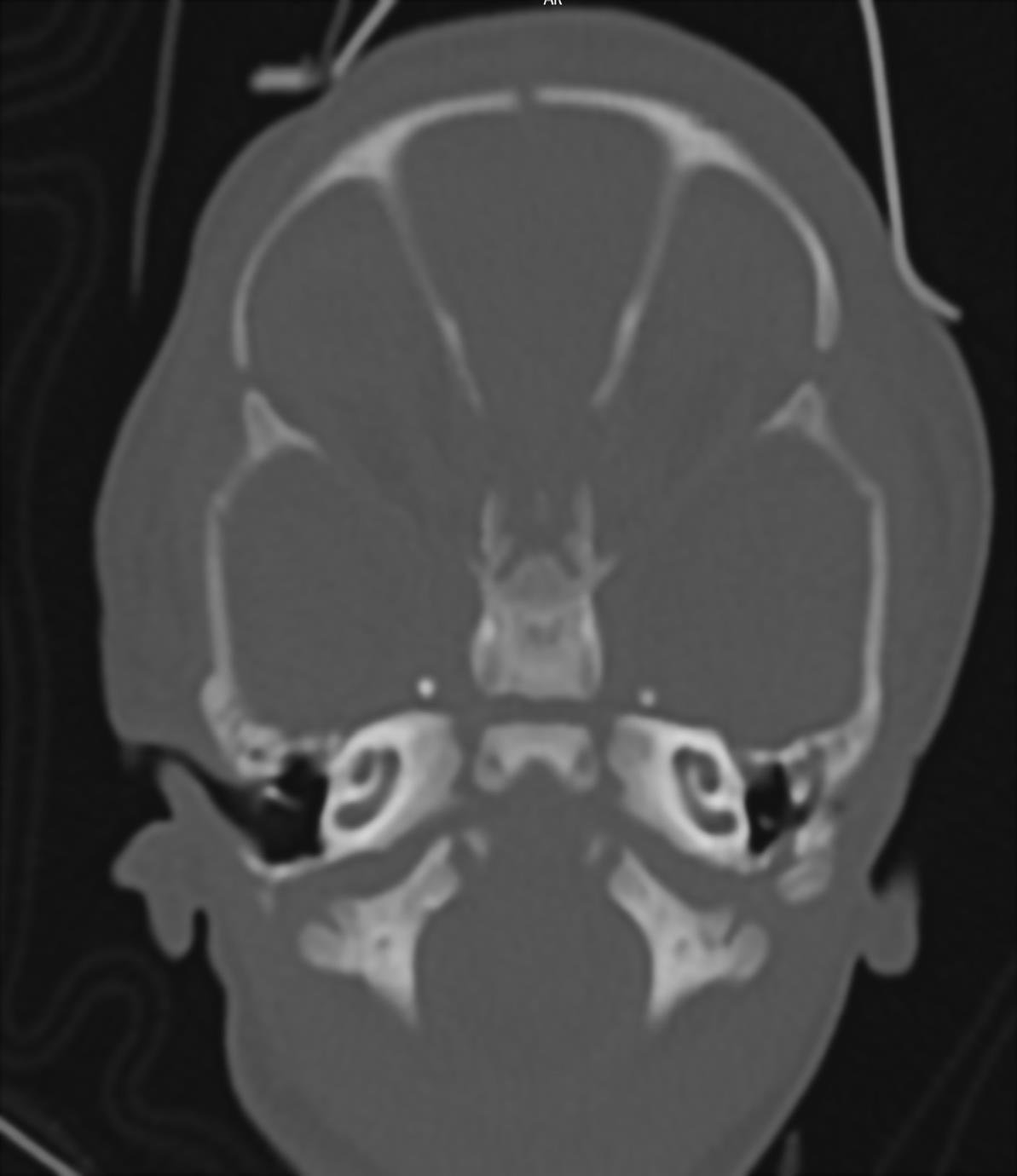
(C) =Coloboma (usually retinochoroidal ) and cranial nerve defects(most common VIII nerve) ( 80 – 90%).
(H) = Heart defects in 75 – 85%, especially tetralogy of Fallot.
(A) = Atresia of the choanae (blocked nasal breathing passages) (50 – 60%).
(R) = Retardation of growth (70 – 80%) and development.
(G) = Genital underdevelopment due to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
(E) = Ear abnormalities and sensorineural hearing loss (>90%).
The cause of CHARGE is usually a new mutation (change) in the CHD7 gene, or rarely, genomic alterations in the region of
chromosome 8q12.2 where the CHD7 gene is located.
Major diagnostic criteria for definite CHARGE syndrome includes: coloboma, choanal atresia, cranial nerve dysfunction(facial
palsy, dysphagia) and CHARGE ear.
Minor criteria includes urogenital and congenital heart defects described above in text.
Definite diagnosis of CHARGE syndrome can be made when four major characteristics or three major characteristics and three mi nor
characteristics are present.
Imaging Findings:
A. A.Clinical Perspective : Clinically the patients present with Interferes with breathing & feeding, ↓ or absent sense
of smell,hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, Asymmetric face or lack of facial expression, Hearing loss,micropenis ,
cryptorchidism,Small labia, uterine abnormality’ delayed or absent puberty & infertility.MRIs and CTs helps to identify
congenital abnormalities in inner ear, cranial nerve involvement or anatomical variation.
A. A. : MRI brain with CT temporal bone cuts helps in diagnosis and as part of pre cochlear implant evaluation. Most
often temporal bone abnormalities are bilateral. Usually these patient presents as agenesis/hypoplasia of one or more
semi – circular canals, more commonly posterior SCC. Other findings include enlarged vestibules, flattened cochlea
with occasionally abnormal shaped cochlea, absence of cochlear nerve.
A. A.Outcome : Many of the structural abnormalities (choanal atresia, heart defects, cleft lip, etc.) can be surgically corrected.
Others, such as feeding problems and speech and language deficits may require years of therapy and other interventions. Some
of the medical specialists who often follow children with CHARGE syndrome include genetics, cardiology, audiology and ENT,
ophthalmology, urology, and endocrinology.
A. A.Take Home Message / Teaching Points:
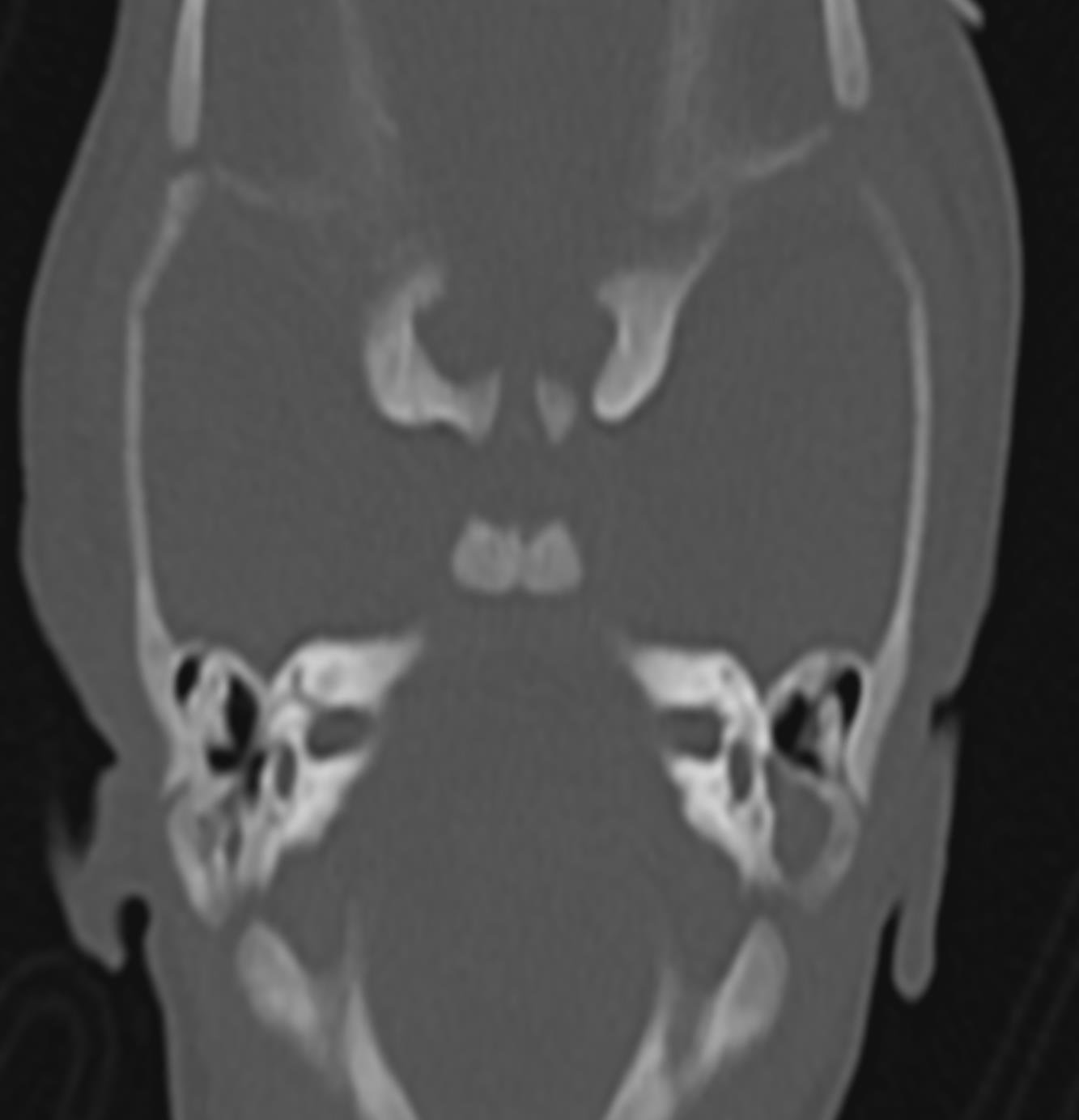
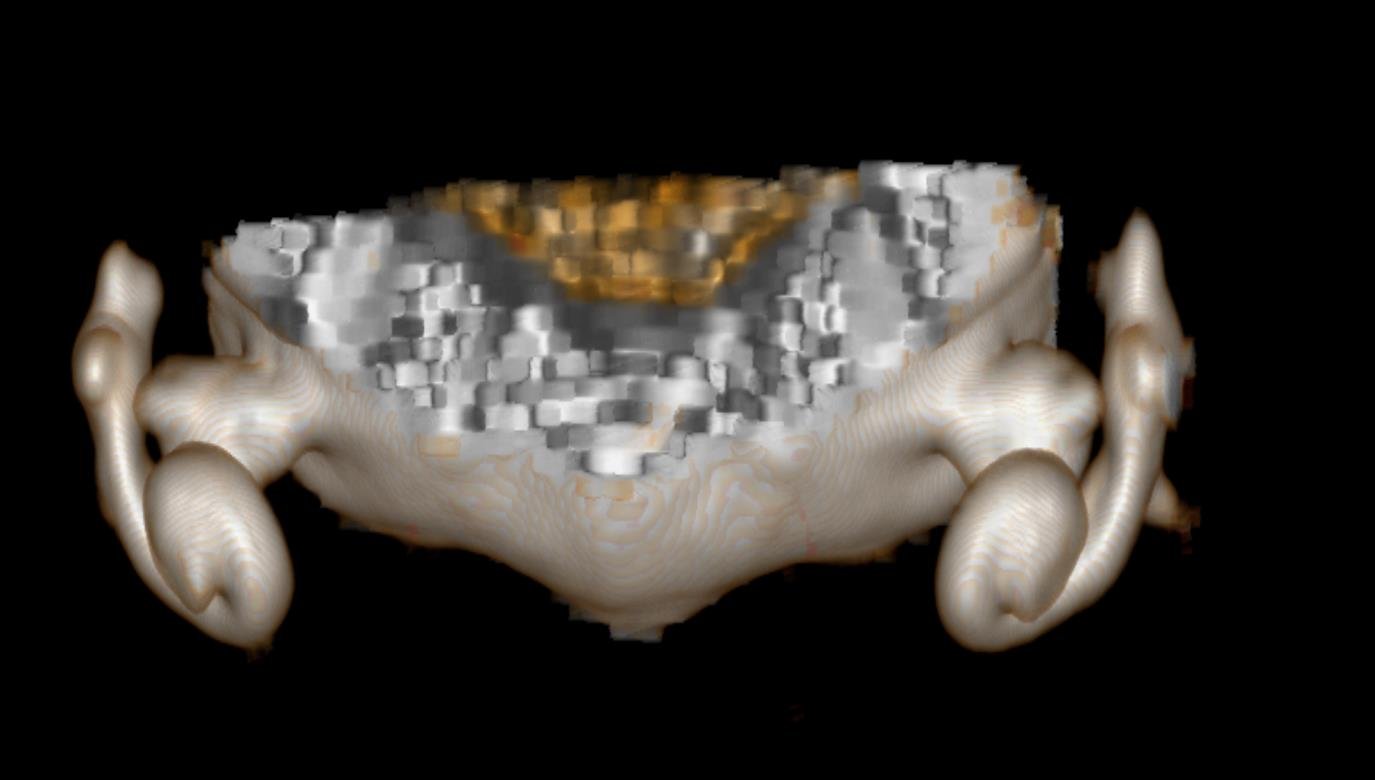
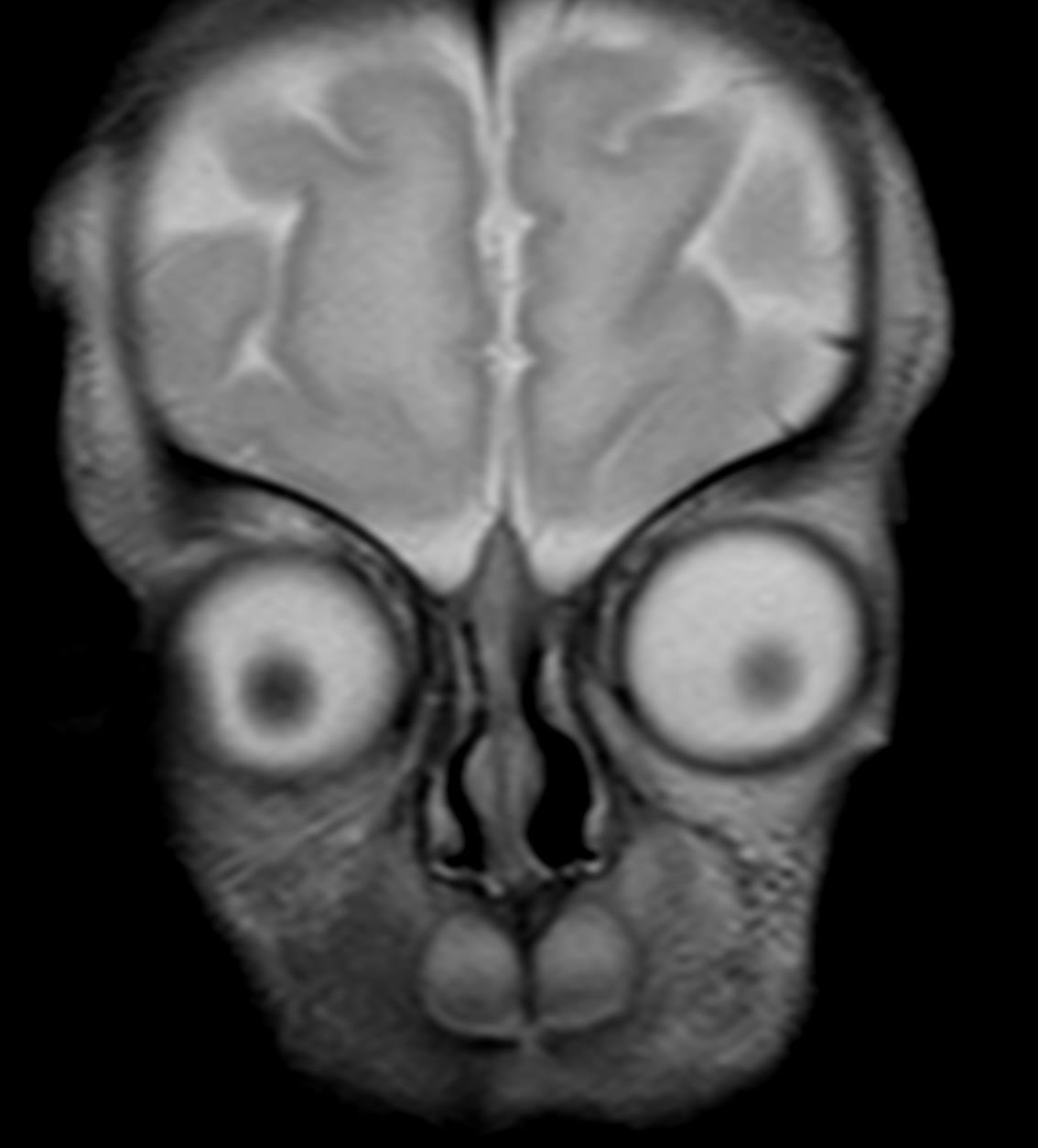
Hypoplasia/agenesis of one or more semi – circular canals, absence of olfactory and facial nerve with coronal clival
cleft in occipital bone ,all these findings on MR concludes the charge syndrome .
Final Diagnosis
CHARGE syndrome.
Differential Diagnosis List
Waardenburg syndrome
Hall – Hittner syndrome
22q11.2 deletion syndrome
Oculo ‐ auriculo ‐ vertebral spectrum
VACTERL association.
References
1.Hsu P, Ma A, Wilson M, et al. CHARGE syndrome: a review. J Paediatr Child Health. 2014;50(7)
2.The 2017
National Child Count of Children and Youth who are Deaf – Blind.” NCDB: The National Consortium on Deaf – Blindness.
20
3.Vissers LE, Van ravenswaaij CM, Admiraal R, et al. Mutations in a new member of the chromodomain gene family
cause CHARGE syndrome. Nat Genet. 2004;36(9):955 – 7.
Figure Captions
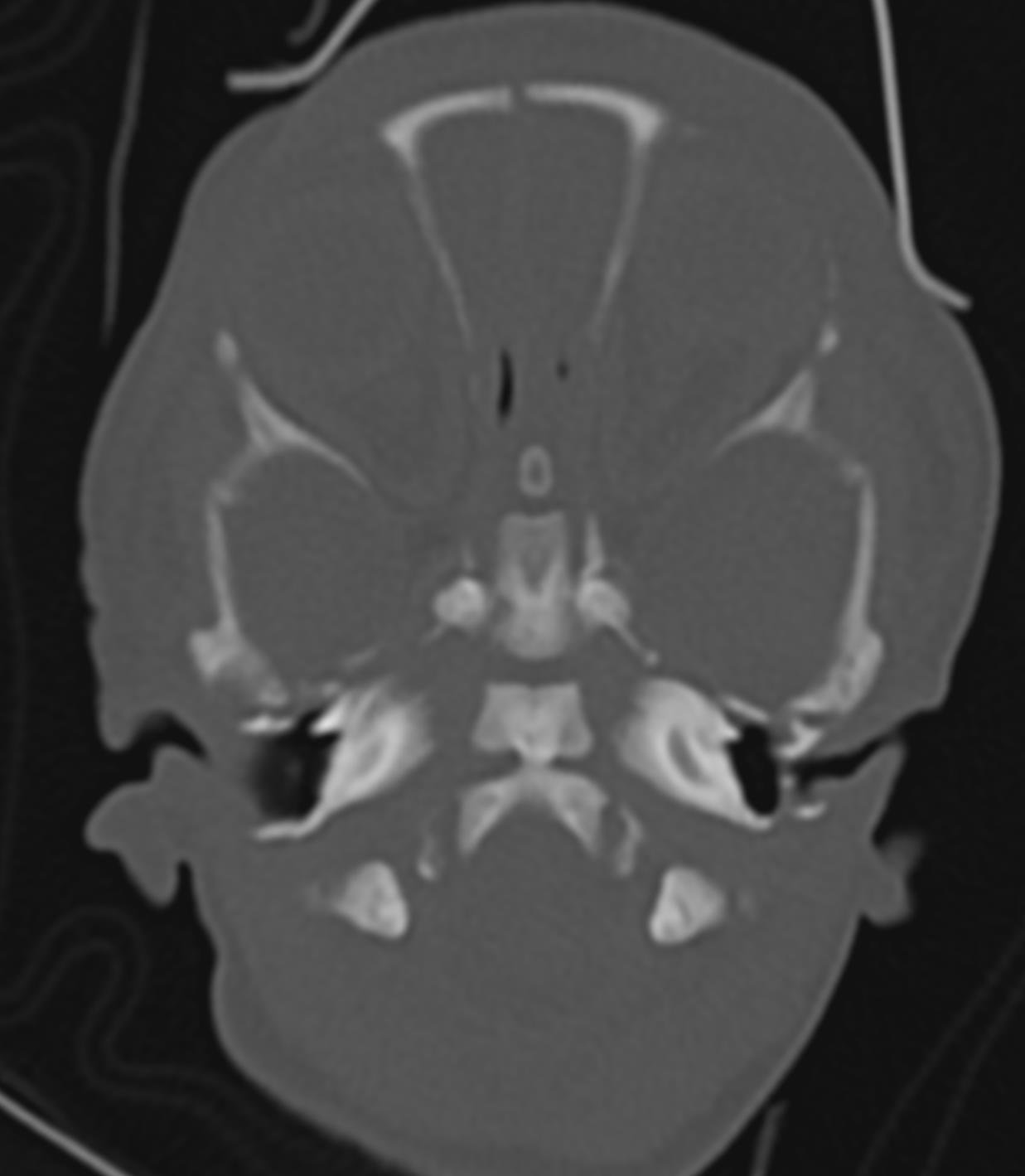
1.FIGURE 1. HRCT axial cuts shows complete aplasia of semi – circular canals on both sides.
2.FIGURE 2. HRCT axial cuts shows coronal clival cleft in occipital bone.
3.FIGURE 3. HRCT axial cuts shows Malformed stapes with aplasia of incus and malleus on both sides.
4.FIGURE 4 . T2W axial MR image shows absence of VII nerve on left side and normal VII and VIII nerve on
right side.
5.FIGURE 5. 3D reconstructed MR image shows incomplete development of semi – circular canals.
6.FIGURE 6: T2W coronal MR image shows absence of olfactory bulb bilaterally.